Mon, 31 Oct 2022 09:39:05 CDT

Low water levels in the Mississippi River have caused grain barge rates to increase, which causes grain buyers at local grain elevators to reduce their bids for grain delivered. When water levels drop in the marine highway system, barge drafts are reduced (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, 2022). A barge draft is the distance between the waterline and boat, or the barge hull structure, and increases with the amount of weight present on the barge. The average barge with a draft of 9 feet can hold 1,500 tons of grain which equates to about 59,000 bushels of corn, 55,000 bushels of soybeans, and 53,500 bushels of rice (USDA-AMS, 2022). Each reduced foot of draft results in 150-200 fewer tons, or anywhere between 5,500 to 7,500 bushels depending on the crop, of grain capacity on a barge (Iowa Soybean Association, 2022). If barge drafts decrease for vessels carrying grain, this means the cost to transport grain downriver, or the grain barge rate, increases since it takes more barges to move the same amount of grain.
Barge freight rates are established by the U.S. Inland Waterway System using a percent of tariff system. Barge freight rates for the Mississippi River at New Madrid, Missouri near Memphis, Tennessee have skyrocketed since the beginning of September (USDA-AMS, 2022). The 3-year average percent of tariff rate indicates weekly barge freight rate tends to oscillate around 400 percent of tariff, or about $12.56/ton. In October 2022, the barge freight rate averaged 2400 percent of tariff, or $75.36/ton, which means the cost to transport grain from Memphis to the port of New Orleans was roughly six times higher than average. The increase in transportation cost is usually reflected in lower cash grain bids at country grain elevators which results in a weakened basis, which is the local cash price received by farmers at the country elevator less the futures price established by the Chicago Board of Trade.
?
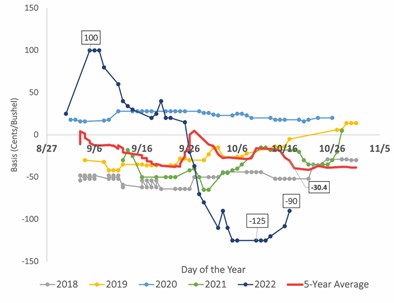
In a technical report recently published by the Fryar Price Risk Management Center of Excellence, Biram, et al. (2022) provide a detailed analysis of how increased barge freight rates weaken basis. Here, we provide a snapshot of how soybean basis has fluctuated in typical harvest months for Helena, Arkansas for the previous five years and show how significant the impact of the low water levels in the Mississippi River has been in recent weeks (Figure 1). As of October 18, 2022, new crop soybean basis at Helena, Arkansas is abnormally low at 90 cents under the front month soybean futures contract (ZSX2) which is nearly 200% below the five-year average during the months of September and October (i.e. 30.4 under). Additionally, basis is relatively more volatile than the five-year average with the strongest basis in this time frame of 100 cents over ZSX2 on September 6, 2022, to the weakest basis of 125 cents under the week of October 5, 2022. The strong basis in early September is primarily due to tight pre-harvest stocks.
We now provide immediate and near-term implications for risk management. In the immediate term, a producer should consider storing grain until the winter months where current cash bids for delivery appear to have stronger basis and to consider the benefit of higher prices at a future delivery date relative to storage costs. Based on historical USDA-AMS data, basis typically improves by 50 cents between harvest months and winter months. Looking to the 2023 growing season, producers should consider revenue insurance such as RP and RP-HPE or to engage in forward contracting which allows a producer to take advantage of stronger basis in the summer months prior to harvest. While revenue crop insurance provides price protection based on futures market prices, it can allow a producer the opportunity to be more aggressive with their forward contracting as they can price more bushels confidently with an additional layer of non-production risk protection (i.e. elevator fees and non-delivery). These tools may be used independently or jointly, and the best risk management strategy for a producer considering these tools may differ across farms.
Credit: Southern Ag Today















