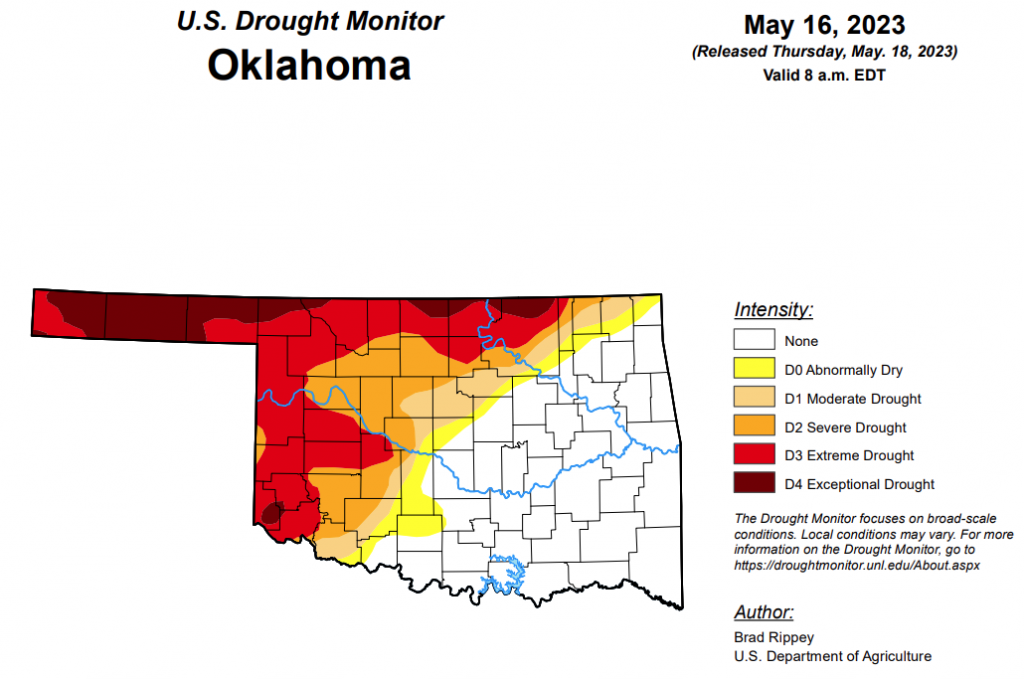
To view the Oklahoma Drought Map, click here.
According to the latest Oklahoma Drought Map, Exceptional drought has decreased from last week’s 10.09 percent and is now at 8.88 percent.
Extreme drought or worse has also improved this week, as it decreased from 33.10 percent last week to 30.67 percent this week.
Severe drought or worse has decreased significantly from last week’s 48.07 percent to this week’s 43.81 percent.
Moderate drought or worse has improved from last week’s 52.47 percent to this week’s 50.19 percent.
Abnormally dry or worse conditions have improved significantly, moving from last week’s 60.81 percent to 55.79 percent this week.
According to the 6-10-day precipitation outlook map, the probability of precipitation increases as the map moves west. The far east side of the state stands as a near normal chance of precipitation through May 27, and that chance increases all the way through the far west side of the panhandle, which is leaning above a 50 to 60 percent chance of precipitation.
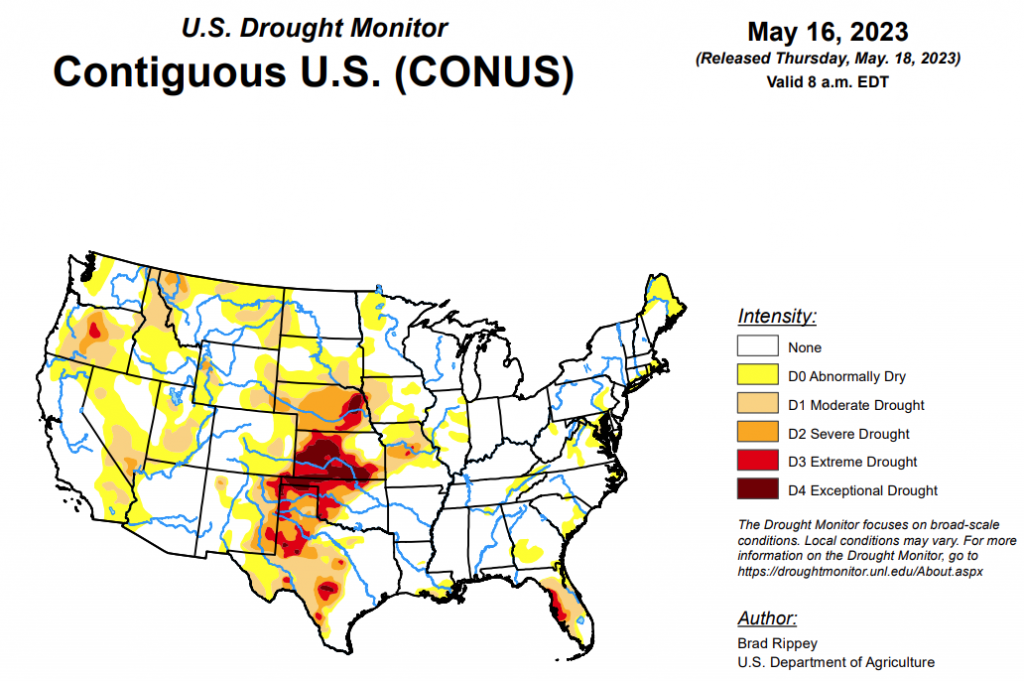
To view the United States Drought Map, click here.
According to the latest U.S. Drought Monitor, a complex, slow-moving storm system delivered heavy rain across much of the nation’s mid-section, but largely bypassed some of the country’s driest areas in southwestern Kansas and western Oklahoma, as well as neighboring areas. Still, the rain broadly provided much-needed moisture for rangeland and pastures, immature winter grains, and emerging summer crops. Significant rain spread into other areas, including the southern and western Corn Belt and the mid-South, generally benefiting crops but slowing fieldwork and leaving pockets of standing water. Excessive rainfall (locally 4 to 8 inches or more) sparked flooding in a few areas, including portions of the western Gulf Coast region. Little or no rain fell across much of the remainder of the country, including southern Florida, the Northeast, the Great Lakes region, and an area stretching from California to the southern Rockies. Warmth in advance of the storm system temporarily boosted temperatures considerably above normal across parts of east-central Plains, western Corn Belt, and upper Great Lakes region. Meanwhile, record-setting heat developed in the Pacific Northwest, setting several May temperature records.
In the Southern Plains, most of the region remained free of drought, but moderate to exceptional drought (D1 to D4) persisted in parts of central and western Texas and across the northwestern half of Oklahoma. During the drought-monitoring period, ending on the morning of May 16, extremely heavy rain drenched the western Gulf Coast region, especially near the central Texas coast. On May 10, Palacios, Texas, measured 6.21 inches of rain—part of a very wet stretch that included an additional 3.93 inches on May 13-14. Heavy showers extended northeastward into southeastern Oklahoma, northern Louisiana, Arkansas, and western Tennessee. By May 14, the U.S. Department of Agriculture reported that topsoil moisture was rated 30% surplus in Arkansas, along with 29% in Louisiana. Farther west, however, serious drought impacts persisted, despite spotty showers. Statewide in Texas, rangeland and pastures were rated 51% very poor to poor on May 14. Any rain was generally too late for the southern Plains’ winter wheat, which is quickly maturing. More than half of the wheat—52 and 51%, respectively, in Texas and Oklahoma—was rated very poor to poor by mid-May. A recent estimate by the U.S. Department of Agriculture indicated that 32.6% of the nation’s winter wheat will be abandoned—highest since 1917—including 70.1% of the Texas crop.
In the High Plains, phenomenal rainfall totals led to significant reductions in drought coverage, especially from eastern Colorado and northwestern Kansas into western North Dakota. Goodland, Kansas, received consecutive daily-record totals of 1.50 and 1.12 inches, respectively, on May 10 and 11. Daily-record totals topped 3 inches on the 11th in Imperial, Nebraska (3.56 inches), and Colorado Springs, Colorado (3.18 inches). That marked the wettest May day on record in Colorado Springs, toppling 2.34 inches on May 30, 1935. In Denver, Colorado, where 2.92 inches fell on the 11th, it was the wettest calendar day since May 6, 1973, when 3.27 inches fell. Denver’s storm total (4.40 inches from May 10-12) represented more than 30 percent of its normal annual precipitation. During the week ending May 14, the U.S. Department of Agriculture reported double-digit improvements in topsoil moisture rated very short to short in several states, including Nebraska (from 66 to 46%), South Dakota (from 38 to 19%), and Colorado (from 45 to 35%). The rain also helped to revive winter wheat and benefited emerging summer crops. Still, even with the rain, Kansas led the nation on May 14 with 68% of its winter wheat rated in very poor to poor condition. In addition, the rampant storminess largely bypassed some of the extreme to exceptional drought (D3 to D4) areas in a strip extending from southwestern Kansas into eastern Nebraska.
Looking ahead, showers and thunderstorms will linger for the next couple of days across the lower Southeast, in the vicinity of a weakening cold front, with an additional 1 to 3 inches of rain possible in some areas. Meanwhile, another cold front will race eastward across the northern U.S., generating showers before reaching the Atlantic Coast on Saturday. Rainfall associated with the Northern cold front will be short-lived, with most locations receiving less than an inch. However, late-week thunderstorms may become heavy along the tail of the cold front, with 1 to 3 inches of rain possible in central and southern sections of the Rockies and Plains. Elsewhere, little or no precipitation will fall during the next 5 days along and near the Pacific Coast. The NWS 6- to 10-day outlook for May 23 – 27 calls for the likelihood of near- or above-normal temperatures and precipitation across most of the country. Cooler-than-normal conditions will be confined to parts of the South, while drier-than-normal weather should be limited to the Pacific Northwest and an area stretching from the mid-South and lower Midwest into the Northeast.
To view the 6-10 Day Precipitation Outlook Map, click here.
To view the 6-10 Day Temperature Outlook Map, click here.
To view the Monthly Drought Outlook Map, click here.















